|
|
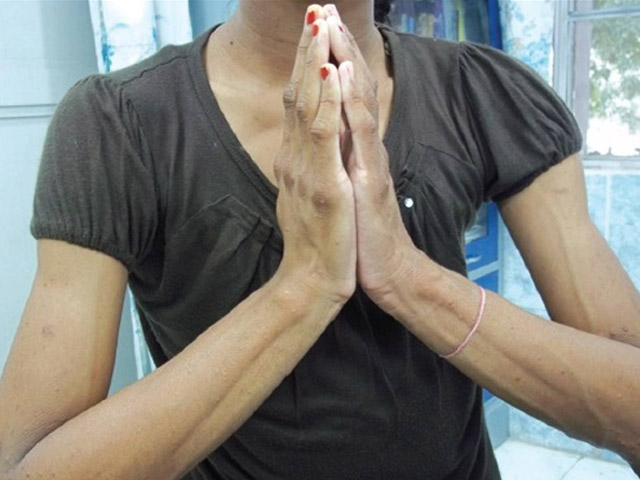
HANDS OF A DIABETIC type 1:
featured with limited joint mobility

HANDS OF A DIABETIC type 1:
features with sclerodactyly (hard waxy skin)
![]() TOP 10 HAND SIGNS
TOP 10 HAND SIGNS
IN DIABETES MELLITUS TYPE 1:
(Ranked by 'Log Odds Ratio' = LOR)
I - Thick, waxy/hardening skin on back of hand (sclerodactyly)
[Diabetes hand sign 6-1: LOR = +4.58]
II - Dry scally palm
[Diabetes hand sign 6-8: LOR = +3.47]
III - Limited joint mobility (LJM)
[Diabetes hand sign 7-1: LOR = +2.98]
IV - Pink patches on back of the hand / fingers (granuloma annulare lesions)
[Diabetes hand sign 6-3: LOR = + 2.73]
V - Shiny patches, first: red-brown & painless, later: yellow & ulceration (necrobiosis lipoidica)
[Diabetes hand sign 6-6: LOR = + 2.71]
VI - Little skin pebbles on back of the hand / fingers (Huntley's papules)
[Diabetes hand sign 6-4: LOR = + 2.64]
VII - Locked finger, a.k.a. 'trigger finger' (stenosing tenosynovitis)
[Diabetes hand sign 7-3: LOR = +2.50]
VIII - Palmar dermatoglyphics: high density on thenar
[Diabetes hand sign 5-13: LOR = + 2.50]
IX - Palmar dermatoglyphics: radial arch on hypothenar
[Diabetes hand sign 5-11: LOR = + 2.47]
IX - Palmar dermatoglyphics: ulnar loop on hypothenar
[Diabetes hand sign 5-11: LOR = + 2.14]
![]() TOP 10 HAND SIGNS
TOP 10 HAND SIGNS
IN DIABETES MELLITUS TYPE 2:
(Ranked by 'Log Odds Ratio' = LOR)
I - Limited joint mobility (LJM)
[Diabetes hand sign 7-1: LOR = +3.36]
II- Terry's nails
[Diabetes hand sign 2-3: LOR = +3.09]
III - Pink patches on back of the hand / fingers (granuloma annulare lesions)
[Diabetes hand sign 6-3: LOR = + 2.73]
IV - Shiny patches, first: red-brown & painless, later: yellow & ulceration (necrobiosis lipoidica)
[Diabetes hand sign 6-6: LOR = + 2.71]
V - Little skin pebbles on back of the hand / fingers (Huntley's papules)
[Diabetes hand sign 6-4: LOR = + 2.64]
VI - Locked finger, a.k.a. 'trigger finger' (stenosing tenosynovitis)
[Diabetes hand sign 7-3: LOR = +2.50]
VII - Palm: radial arch on hypothenar
[Diabetes hand sign 5-11: LOR = + 2.28]
VIII - Simian line
[Diabetes hand sign 4-1: LOR = +2.24]
IX - Palmar dermatoglyphics: high density on thenar
[Diabetes hand sign 5-13: LOR = + 2.50]
X - Palmar dermatoglyphics: radial arch on hypothenar
[Diabetes hand sign 5-11: LOR = + 2.47]
These TOP 10 hand signs for Diabetes Mellitus type 1 & 2 show that skin abnormalities (combined with motoric problems) play a key role in recognizing Diabetes Mellitus.
NOTICE: Log Odds Ratios are calculated from the prevalence (%) among Diabetes patients & controls; more details are presented in the right column at the bottom of this page.
![]() HAND SIGNS & HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
HAND SIGNS & HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
• Hand signs in DOWN SYNDROME!
_- Down syndrome case study 1
_- Down syndrome case study 2
• Hand signs in FRAGILE-X SYNDROME!
_- Fragile-X syndrome case study 1
_- Fragile-X syndrome case study 2
_(In people with autism 2% to 6% have Fragile-X syndrome!)
• Hand signs in DIABETES MELLITUS!
• Hand signs in RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS!
• Hand signs in PSORIASIS!
• Hand signs in SCHIZOPHRENIA!
![]() HAND TEST:
HAND TEST:
• MARFAN SYNDROME hand test!
![]() BIG FIVE PERSONALITY DIMENSIONS:
BIG FIVE PERSONALITY DIMENSIONS:
• Hand constellations in Agreeableness!
• Hand constellations in Conscientiousness!
• Hand constellations in Extraversion!
• Hand constellations in Neuroticism!
• Hand constellations in Openness!
![]() SIMIAN LINE INDEX:
SIMIAN LINE INDEX:
INTRO: About the Simian Line (a.k.a. 'simian crease')
• HOW TO RECOGNIZE a 'complete' Simian Line?
• WHY PALM CREASE NAMED the Simian Line?
• BRIEF HISTORY of the Simian Line
• ETHNIC POPULATIONS & the Simian Line
• MEDICAL PROBLEMS & the Simian Line
• PSYCHOLOGY & the Simian Line
• PROJECTS related to the Simian Line
• SYNONYMS for the Simian Line
• FAMOUS Simian Line holders
![]() MORE HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
MORE HAND DIAGNOSTICS:
• Understanding hand shape!
• The hand lines (palmar creases)
• The Sydney line
• Fingerprints (+ dermatoglyphics)
• The Hypothenar whorl
• What can finger length reveal?
• The 5th finger (pinky)
• The fingernail tutor
• The hand sign tutor: 300+ hand signs! [via 9 hand levels]
Diabetes Mellitus & the hand:
35 Hand Signs!
(Including e.g. the 'diabetic stiff-hand syndrome')
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar. Regarding the hand, scientific studies have pointed out that the so-called 'diabetic stiff-hand syndrome' (a.k.a. diabetic cheiroarthropathy) characterized by stiffness (without the joints directly getting involved) and thickening of skin, is recognized to represent a common complication in the later stages of the disease of both diabetes mellitus type 1 (up to 50%) and type 2 (up to 75%).20 Actually, there is a large group of significant hand signs that may represent a clue for diabetes mellitus type 1 and/or type 2. This article presents an overview of 35 individual hand signs that are significant for diabetes mellitus (featured with illustrative statistics).
The statistics indicate for both forms (type 1 & type 2) that the development of diabetes mellitus typically manifests inside the hand with especially abnormalities in the skin quality (and/or fingernails) & motorics; though of much lesser concern, also dermatoglyphics (in the lower palm) & major palmar creases may present significant clues!
Diabetes Mellitus TYPE 1:
1 - Thick, waxy skin (sclerodactyly) [Diabetes h.s. 6-1: LOR = +4.58]
2 - Dry scally palm [Diabetes hand sign 6-8: LOR = +3.47]
3 - Limited joint mobility [Diabetes hand sign 7-1: LOR = +2.98]
4 - Pink patches on back of hand [Diabetes hand sign 6-3: LOR = + 2.73]
5 - Shiny patches on back of hand [Diabetes h.s. 6-6: LOR = + 2.71]
Diabetes Mellitus TYPE 2:
1 - Limited joint mobility [Diabetes hand sign 7-1: LOR = +3.36]
2 - Half white, half pink nails [Diabetes hand sign 2-3: LOR = +3.09]
3 - Pink patches on back of hand [Diabetes hand sign 6-3: LOR = + 2.73]
4 - Shiny patches on back of hand [Diabetes h.s. 6-6: LOR = + 2.71]
5 - Little pebbles on back of hand [Diabetes h.s. 6-6: LOR = + 2.64]
• 35 Hand signs significant for Diabetes Mellitus
• The TOP 10 Hand signs in respective Diabetes Mellitus type 1 & 2!
• How to make a hand-diagnosis for Diabetes Mellitus: 4 requirements!

How to make a Palm Reading Assessment for DIABETES MELLITUS (Type 1 & 2) Key-elements of the hand in Diabetes Mellitus (type 1 & 2) in a nutshell: skin / nail problems and or motoric problems, palmar dermatoglyphic stereotypes below the ring finger & the hypothenar, high occurence of the simian crease. 
[Phantom picture for Diabetes Type 1 & 2 will be available later] Studies have shown that there not much difference between recognizing diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2 from the hand only. An advanced hand diagnosis for Diabetes Mellitus requires a person to have multiple significant hand markers that follow the MAJOR REQUIREMENT + the additional requirements described below: MAJOR REQUIREMENT: The person requires to have significant hand markers for Diabetes Mellitus in at least three out of the seven dimensions of the hand; most likely a combination of the dimensions: SKIN QUALITY, FINGERNAILS, MOTORICS & DERMATOGLYPHICS. - ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENT A: The person requires to have at least one hand marker that relates to one of the following two perspectives: SKIN QUALITY (= hand perspective 6) or MOTORICS (= hand perspective 7) - ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENT B: The person requires to have at least one hand marker that relates to FINGERNAILS (= hand perspective 2), DERMATOGLYPHICS (= hand perspective 5) or HAND LINES (= hand perspective 4). - ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENT C: The person requires to have at least one hand marker in the palm (or back of the hand) + at least one hand marker in the fingers. IMPORTANT: Even when all above REQUIREMENTS are fullfilled, then one can still NOT speak of a 'confirmed' hand diagnosis for Diabetes Mellitus: an additional health assessment beyond the hand is still requirement! Some of the 35 significant hand markers for Diabetes Mellitus that are listed below became known in medical science as a 'physical minor anomaly' (such as the simian crease & the Sydney line). But in general most of these individual hand markers can usually be described as harmless body characteristics - except for the markers described for perspectives 2, 6 and 7. • Hand perspective 1 - HAND SHAPE: - 1-1: Appearent hand shape asymmetry. • Hand perspective 2 - FINGERNAILS: - 2-1: Fungal infection of the nail (onychomycosis); - 2-2: Redness in proximal nail fold (chronic paronychia); - 2-3: White nail with small pink/brown distal band (Terry's nails); - 2-4: Blue lunula; - 2-5: Yellow nails + yellow skin; - 2-6: Spoon nail (koilonychia). • Hand perspective 3 - FINGER MORPHOLOGY: - 3-1: High finger length asymmetry: e.g. 2D:4D asymmetry. • Hand perspective 4 - MAJOR LINES: - 4-1: Simian crease; - 4-2: Sydney line. • Hand perspective 5 - DERMATOGLYPHICS: - 5-1: Fingers: radial loop on ringfinger; - 5-2: Fingers: radial loop on pinky; - 5-3: Fingers: high thumb minus pinky ridge count (high MD15); - 5-4: Palm: triradius c below ring finger is missing; - 5-5: Palm: ridge line C ends below ring finger (abbortive ridge line C); - 5-6: Palm: a-b ridge count summarized for both hands < 70 (ridge count between triradius below index finger & triradius below middle finger); - 5-7: Palm: 2 or 3 triradii on hypothenar; - 5-8: Palm: high positioned axial triradius; - 5-9: Palm: triradius t is missing; - 5-10: Palm: ulnar loop on hypothenar; - 5-11: Palm: radial arch on hypothenar; - 5-12: Palm: pattern in the hypothenar OR thenar of just one hand; - 5-13: Palm: high density on thenar. • Hand perspective 6 - SKIN QUALITY: - 6-1: Thick, waxy/thickening skin on back of the hand (sclerodactyly); - 6-2: Infections; - 6-3: Pink patches on back of the hand / fingers (granuloma annulare lesions); - 6-4: Little skin pebbles on back of the hand / fingers (Huntley's papules); - 6-5: Blisters (bullosis diabeticorum); - 6-6: Shiny patches, first: red-brown & painless, later: yellow & ulceration (necrobiosis lipoidica); - 6-7: Dramatic appearing hand infections (e.g. Tropical Diabetic Hand Syndrome). - 6-8: Dry scally palms. • Hand perspective 7 - MOTORICS: - 7-1: Neuropathy: loss of function, loss of movement / sensation (Tinel's sign, Phalen's test, preacher sign / prayer sign, limited joint mobility); - 7-2: Contracture of pinky and/or ring finger (Dupuytren's contracture); - 7-3: Locked finger, a.k.a. 'trigger finger' (stenosing tenosynovitis); - 7-4: Numbness, tingling and/or pain (Carpal Tunnel Syndrome); NOTICE: About 3% of the world population has diabetes mellitus, of which about 2.7% concerns Type 2 and 0.3% concerns Type 1. But in Down syndrome the occurence of diabetes type 1 is much higher (estimates indicate at least 4x times higher to up to 10%), therefore it is interesting to notice that 8 of the 26 hand markers in Down syndrome are also seen in the summary of hand markers for Diabetes Mellitus! The hand in RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS The hand in PSORIASIS The hand in DOWN SYNDROME The hand in FRAGILE-X SYNDROME Fingernails problems in Diabetes Mellitus |
THE FAMOUS 'SIMIAN LINE' (SINGLE PALMAR CREASE) IS ONLY A MINOR KEY-ELEMENT FOR THE HAND IN DIABETES MELLITUS (TYPE 2)
the Simian Line & Diabetes Mellitus!
Various studies around the world have proven that the simian line is more often seen among diabetics than in the general population (about 3% of the healthy population has a simian line in at least one hand). This implicates that the simian line is much more important in the genetic syndromes (e.g. Down syndrome & Fragile-X syndrome) than in Diabetes Mellitus - but still, combined with other relevant hand markers the simian line can play a role in a hand diagnosis for Diabetes Mellitus.
This raises the question: 'how can the simian line serve as a diagnostic marker specific for Diabetes Mellitus?'
'Phantom picture' of the hand in Diabetes type 2.

NOTICE: Later the author will present a comprehensive 'phantom picture' for the most typical hand-characteristics in Diabetes Mellitus.
HAND SHAPE & Diabetes Mellitus:
• 1-1 - Apparent hand shape asymmetry
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: ? %; controls: ? % LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
FINGERNAILS & Diabetes Mellitus:
• 2-1 - Fungal infection of the nail (onychomycosis)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: 17-36 %; controls: 6.8-7.0 % 1 LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.57 (average) | ||
• 2-2 - Redness in proximal nail fold (chronic paronychia)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: 10.0 %; controls: +3.0 % 2 LOG ODDS RATIO: 1.28 (average) | ||
• 2-3 - Terry's nails (white nail with small pink/brown distal band)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 2 patients: 10.0 %; controls: 0.5 % (rare in young people) 3 LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: +3.09 (average) | ||
• 2-4 - Blue lunulae
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: ? %; controls: ? % 4 LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
• 2-5 - Yellow nails + yellow skin
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: ? %; controls: ? % LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
• 2-6 - Spoon nail (koilonychia)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: ? %; controls: ? % LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
FINGER LENGTH & Diabetes Mellitus:
• 3-1 - High finger length asymmetry: e.g. 2D:4D asymmetry
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: ? %; controls: ? % LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
HAND LINES & Diabetes Mellitus:
• 4-1 - Simian crease
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: males: 2.3-12.93 %, females: 1.0-12.0 %; controls: 0.3-2.0 % & 0.4-1.0 % 5-7 - Diabetic type 2 patients: males: 3.8-13.33 %, females: 0-14.23 %; controls: 0.3-2.0 % & 0.4-1.0 % 5-8,21 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: +2.12 (average) LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: +2.24 (average) | ||
• 4-2 - Sydney line
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: males: 0.8, females: 4.0 %; controls: 3.8 % & 1.7 % 6 - Diabetic type 2 patients: males: 0, females: 7.6 %; controls: 3.8 % & 1.7 % 6 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1 (females only): +0.87 LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: +0.34 (average) | ||
DERMATOGLYPHICS & Diabetes Mellitus:
• 5-1 - Fingerprints: radial loop on ringfinger
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients (confirmed by glucose tolerance test): 6.2 %; controls: 0.3 % 7 LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.09 | ||
• 5-2 - Fingerprints: radial loop on pinky
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients (confirmed by glucose tolerance test): 2.3 %; controls: 0 % 7 LOG ODDS RATIO: +3.16 | ||
• 5-3 - Fingerprints: high thumb minus pinky ridge count (high MD15)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 2 patients: ? %; controls: ? % LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
• 5-4 - Palm: triradius c below ring finger is missing (= missing c triradius)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: 3.0-8.7 %; controls: 3.1-3.0 % 5-7 - Diabetic type 2 patients: 4.5-15.9 %; controls: 3.1-3.0 % 5-7 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: +0.69 (average) LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: +1.28 (average) | ||
• 5-5 - Palm: ridge line C ends below ring finger (abortive ridge line C)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: 0.5-36.6 %; controls: 0.4-8.0 % 5-7 - Diabetic type 2 patients: 1.3-34.6 %; controls: 0.4-8.0 % 5-7 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: +1.65 (average) LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: +1.61 (average) | ||
• 5-6 - Palm: a-b ridge count summarized for both hands < 70 (ridge count between triradius below index finger & triradius below middle finger)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: ? %; controls: ? % 5,6,10 - Diabetic type 2 patients: ? %; controls: ? % 5,6,10 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: ? (unknown) LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: ? (unknown) | ||
• 5-7 - Palm: 2 or 3 triradii on hypothenar
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: ? %; controls: ? % 5,6,10 - Diabetic type 2 patients: ? %; controls: ? % 5,6,10 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: ? (unknown) LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: ? (unknown) | ||
• 5-8 - Palm: high positioned axial triradius
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: ? %; controls: ? % 5,6,10 - Diabetic type 2 patients: ? %; controls: ? % 5,6,10 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: ? (unknown) LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: ? (unknown) | ||
• 5-9 - Palm: triradius t is missing
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: 0.75 %; controls: 0.5 % 5 - Diabetic type 2 patients: 3.95 %; controls: 0.5 % 5 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: +0.41 LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: +2.10 | ||
• 5-10 - Palm: ulnar loop on hypothenar
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: 13.5 %; controls: 1.8 % 5 - Diabetic type 2 patients: 11.6 %; controls: 1.8 % 5 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: +2.14 LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: +1.97 | ||
• 5-11 - Palm: radial arch on hypothenar
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: 5.6 %; controls: 0.5 % 5 - Diabetic type 2 patients: 4.7 %; controls: 0.5 % 5 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: +2.47 LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: +2.28 | ||
• 5-12 - Palm: pattern in the hypothenar OR thenar of just one hand
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients (confirmed by glucose tolerance test): 36.7 %; controls: 9.9 % 7 LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.67 | ||
• 5-13 - Palm: high density on thenar
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: 39.1 %; controls: 5.0 % 5 - Diabetic type 2 patients: 31.8 %; controls: 5.0 % 5 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: +2.50 LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: +2.19 | ||
SKIN QUALITY & Diabetes Mellitus:
• 6-1 - Thick, waxy/hardening skin on back of the hand (sclerodactyly)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: 33 %; controls: 0.5 % (rare) 16,17 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: +4.58 | ||
• 6-2 - Infections
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: ? %; controls: ? % LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
• 6-3 - Pink patches on back of the hand / fingers (granuloma annulare lesions)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: 3 %; controls: 0.2 % 18 LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.73 | ||
• 6-4 - Little skin pebbles on back of the hand / fingers (Huntley's papules)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: 72-75 %; controls: 12-21 % 15 LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.64 | ||
• 6-5 - Blisters (bullosis diabeticorum)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: ? %; controls: ? % 14,18 LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
• 6-6 - Shiny patches, first: red-brown & painless, later: yellow & ulceration (necrobiosis lipoidica)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: 7 %; controls: 0.5 % (rare) LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.71 | ||
• 6-7 - Dramatic appearing hand infections (e.g. Tropical Diabetic Hand Syndrome)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: ? %; controls: ? % LOG ODDS RATIO: ? (unknown) | ||
• 6-8 - Dry scally palms
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients type 1: 21 %; controls: 0.8 % 19 LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: +3.47 | ||
MOTORICS & Diabetes Mellitus:
• 7-1 - Limited joint mobility (LJM): neuropathy, loss of function: movement / sensation; a.k.a. diabetic hand syndrome or cheiroarthropathy (e.g. associated with: Tinel's sign, Phalen's test, preacher sign / prayer sign)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic type 1 patients: 20-66 %; controls: 4 % 11,12,13 (+22) - Diabetic type 2 patients: 33-76 %; controls: 4 % 11,12,13 (+22) LOG ODDS RATIO type 1: +2.98 (average) LOG ODDS RATIO type 2: +3.36 (average) | ||
• 7-2 - Contracture of pinky and/or ring finger (Dupuytren's contracture)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: 3-32 %; controls: 1-7 % 14,22 LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.31 (average) | ||
• 7-3 - Locked finger, a.k.a. 'trigger finger' (stenosing tenosynovitis)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: 10-20 %; controls: 1-2 % 14,22 LOG ODDS RATIO: +2.50 | ||
• 7-4 - Numbness, tingling and/or pain (Carpal Tunnel Syndrome)
|
Prevalence: - Diabetic patients: 11-21 %; controls: 5 % 14 LOG ODDS RATIO: +1.28 (average) | ||
SOURCES:
1) The prevalence and management of onychomycosis in diabetic patients. A.K. Gupta et al., 2000
2) Infections and Diabetes: Mechanisms and Prospects for Prevention. P. Pozzilli & R.G.D. Leslie., 1994
3) Comparative study on secondary structural changes in diabetic and non-diabetic human finger nail specimen by using FTIR spectra. K.M. Farhan, 2010
4) Abnormalities of the lunula. M.E. Williams, 2009
5) Dermatoglyphics in diabetes mellitus of type 2 (T2DM) or non-insulindependent. A. Tarca, 2006
6) Digital and palmar dermatoglyphics in diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis and essential hypertension. G.F. Floris, et al., 2000
7) Association between diabetes mellitus and dermatoglyphics. M.R. Chakravartti, 1967 (in: Hautleisten und Krankheiten - Hirsch, 1967 / Hautleistenfibel - A. Rodewald & H. Zankl, 1981)
8) Dermatoglphics study of 210 patients with diabetes mellitus. Li Yanhua Wu Shoushan Han Li Guo Qingmei He Liping, 1990
9) A fingerprint marker from early gestation associated with diabetes in middle age: The Dutch Hunger Winter Families Study. H.S. Kahn et al., 2008
10) Dermatoglyphics in Type 1 diabetes mellitus. A.G. Ziegler et al., 2009
11) Dupuytren's disease, carpal tunnel syndrome, trigger finger, and diabetes mellitus. M. Chammas et al., 1995
12) Reduced Prevalence of Limited Joint Mobility in Type 1 Diabetes in a U.K. Clinic Population Over a 20-Year Period. J.R. Lindsay et al., 2005
13) Limited joint mobility (LJM) of the hand in patients with diabetes mellitus: relation to chronic complications. H.S. Starkman et al, 1986
14) Hand manifestations of diabetes mellitus. P.G. Fitzgibbons & A-P C. Weiss, 1995
15) Finger pebbles: a dermatologic sign of diabetes mellitus. D.S. Hollister et al., 2000
16) Updates in the Management of Cutaneous Manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus. A.S. Hayat et al., 2010
17) Scleredema and diabetic sclerodactyly. Lisa Moed Gruson & Andrew Franks, 2005
18) Localized granuloma annulare is associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. M.F. Muhlemann & D.R.R. Williams, 2006
19) The Prevalence of Cutaneous Manifestations in IDDM Patients and Their Association With Diabetes Risk Factors and Microvascular Complications G. YOSIPOVITCH et al, 1998
20) The specificity of capillaroscopic pattern in connective autoimmune diseases. A comparison with microvascular changes in diseases of social importance: arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus S.N. Lambova & U. Müller-Ladner, 2009
21) Study of Dermatoglyphics in Patients with Type II Diabetes Mellitus Essential Hypertension in the Age Group between 35-55 Years. S. Sumathi & S.D. Desai, 2007
22) Hand disorders associated with diabetes : a review. A. Zyluk & P. Puchalski, 2015
|
|
© COPYRIGHT 2002-2017: |
